Trade and Transport in Eswatini, Manzini, Lobamba
Business in Eswatini (Swaziland) Manzini, Lobamba, Mbabane, Logistics

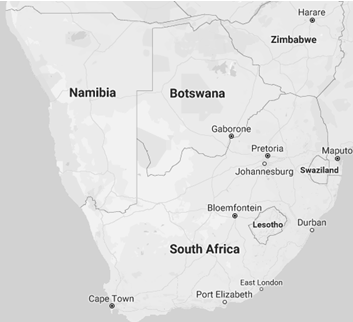
The Kingdom of Eswatini (Swaziland) is a Southern African landlocked country
- Umbuso we Swatini in Swati language
- Mbabane is the administrative, economic and commercial capital of Eswatini and the largest Liswati city
- Lobamba is the royal capital of Eswatini (Swaziland)
- Largest cities of Eswatini (Swaziland): Manzini (second largest Liswati city), Mbabane, Nhlangano and Siteki
- Other Swazi cities are Ezulwini, Matsapha, Hlatikhulu, Pigg's Peak, Simunye and Big Bend
- Eswatini (Swaziland) is a lower middle-income developing country
- Main Swazi economic activities: mining (diamonds, coal, gold... 13% of the GDP), agribusiness (agriculture: sugar, sugar cane, cotton, tobacco, rice, corn), transport, tourism and manufacturing industry (textiles)
- Services: 50% of the GDP
- Unemployment: 34% of the population
- 75% of the population work in subsistence agriculture in the Lands of the Swazi Nation
- Largest trading partners: South Africa, the United States and the EU
- Borders of Eswatini: South Africa (430 kilometres) and Mozambique (105 kilometres)


Transport and Logistics in Eswatini
- National Road network: 1,500 kilometres
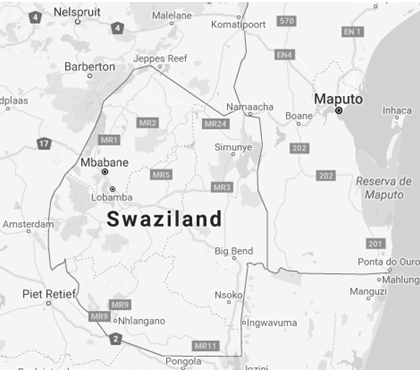
- MR1 Mbabane - Piggs Peak - Jeppes Reef (border with South Africa)
- MR3 Ngwenya, border with South Africa - Mbabane - Manzini - Hlane - Lomashasha, border with Mozambique - is the most important road.
- MR8 Manzini - Big Bend - Lavumisa, border with South Africa.
- MR9 Manzini - Nhlangano - Mahamba, border with South Africa.
- MR11 Nhlangano - Lavumisa, border with South Africa.
- MR19 Mbabane - Nertson, border with South Africa.
- Sikhuphe International Airport
- Nearest ports

 Swazi Students from Eswatini
Swazi Students from Eswatini


More information: International Trade and Business in Eswatini, at EENI Global Business School Website.

Trade and Business Organisations
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
- COMESA-EAC-SADC Agreement
- SACU
- India-SACU Agreement
- Commonwealth

- African Development Bank
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa

- Swazi population: 1,4 million inhabitants
- Population density of Eswatini: 82.7 inhabitants / km²
- 26% of the adult Swazi population is infected with HIV / AIDS
- Area of Eswatini is of 17.363 km²
- Eswatini is less than 200 kilometres from north to south and 130 kilometres from east to west
- Eswatini is one of the smallest African countries
- Several rivers cross Eswatini, such as the Great Usutu River, Lubombo (eastern border with Mozambique), Ngwavuma and Mbuluzi
- Eswatini is an absolutist Monarchy
- King (Head of state): Mswati III (Ngwenyama)
- Eswatini obtained its Independence from the United Kingdom in 1968
- Calling code of Eswatini: 268
- Code top-level domain of Eswatini: .sz
- Currency of Eswatini: Lilangeni (SZL)
- Lilangeni is anchored to the South African Rand
The four districts of Eswatini are:
Swazi Region: Hhohho
- Capital: Mbabane
- Area: 3,625
- Population: 0.3
Swazi Region: Lubombo
- Capital: Siteki
- Area: 5,849
- Population: 0.2
Swazi Region: Manzini
- Capital: Manzini
- Area: 4,093
- Population: 0.3
Swazi Region: Shiselweni
- Capital: Nhlangano
- Area: 3,786
- Population: 0.2
(population in a million people)
Swazis are the main Swazi ethnic group (84% of the population)
- Zulu: 10% of the population
- Tsona: 3% of the population
- Small population of white Africans (British and Afrikaners descendants)

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religions in Eswatini
- Christianity (88% of Swazi)
- African Traditional Religions
Languages of Eswatini
The official languages of Eswatini are SiSwati and English (language of business, press, education).
- 2.5 million people speak SiSwati
- SiSwati (Swati) is a Bantu language of Nguni group
- SiSwati is spoken in Eswatini and South Africa (one of the official languages)
Other spoken languages in Eswatini are Zulu and Tsonga.
Portuguese has been introduced as a third language in schools, due to its proximity to Mozambique.
History of Eswatini (Swaziland)
- 27,000 years: prehistoric rock art paintings
- The first known inhabitants were the Khoisan hunter-gatherers (Bantu migrations)
- 4th century: introduction of agriculture
- 11th century: Sotho and Nguni ancestral languages
- Swazi settlers
- Ngwane village (King Sobhuza I, capital in Zombodze)
- 19th century: unification of the territory by King Mswati II
- 1903: after the British victory in the Anglo-Boer War, Eswatini became a British protectorate
- 1968: independence (United Kingdom)
Higher Education in Eswatini
Ministry of Education of Eswatini
- University of Eswatini
- Nazarene University of South Africa
- Christian University of Eswatini
- Campus of the University of Creative Technology of Limkokwing (Mbabane)
- University College of Technology of Eswatini
 Suazilandia
Suazilandia
 Eswatini
Eswatini
 Suazilandia
Suazilandia


 Tweet
Tweet