Foreign Trade and Transport in Cameroon, Yaoundé
Business in Cameroon, Douala, Yaoundé, Bafoussam, Bamenda, Marua

Cameroon is a Central African country
- The political and administrative capital of Cameroon is Yaoundé (2.7 million inhabitants)
- The Cameroonian economic capital is Douala
- Other largest Cameroonian cities are Bamenda, Garoua, Marua, Bafoussam and Ngaoundéré
- The Cameroonian GDP per inhabitant (parity of purchasing power): 2,300 Dollars, one of the ten first economies in Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Main Cameroonian agricultural products are bananas, cocoa, coffee, cotton, honey
- Cameroon has important petroleum, mining and forestry resources
- Corruption is often a significant problem in Cameroon
- The Cameroonian informal sector represents 75% of the urban labour
- Boko Haram (Jihadist terrorist group from Nigeria)
- Cameroon has borders with the Central African Republic (797 kilometres), the Republic of the Congo (523 kilometres), Gabon (298 kilometres, Oyem), Equatorial Guinea (189 kilometres), Nigeria (1,690 kilometres, Maiduguri) and Chad (1,094 kilometres, Kousséri is 10 kilometres away N'Djamena)
 Cameroonian Students from Cameroon
Cameroonian Students from Cameroon


More information: International Trade and Business in Cameroon, at EENI Global Business School Website.

Transport and Logistics in Cameroon
The port of Douala is the largest Cameroonian port.

Others ports: ports of Limbé and Kribi
A river port in Garoua (seasonal, Bénoué River)
International airports
- Douala
- Yaoundé-Nsimalen
- Garoua
- Marua
Cameroon has 50,000 kilometres of Roads (6,000 asphalted).
- National Road 1 starts in Yaoundé until Kousséri and Fotoko in the North Extreme province.
- National Road 2 goes toward the South of the capital toward Ambam before continuing toward Gabon and Equatorial Guinea.
- National Road 3, the busiest and more dangerous of Cameroon, covers the distance between Yaoundé and Douala.
- National Road 4 it goes north-west to Bafoussam (West province).
- National Road 9, does not go through the capital, starts in Mbalmayo and goes to the cities of Sangmélima, Djoum and Mintom, in the Southern Province.
- National Road 10 goes to the East of Yaoundé, to Ayos and finally to Bonis in the East province.
Roads to:
- Tripoli-Windhoek Transport Corridor
- Trans-Sahelian Road (Dakar-Cameroon-N'Djamena Corridor)
- Lagos-Mombasa Transport Corridor
Cameroonian Railroad Network
- Railway: 1,020 kilometres
- Trans-Cameroonian (Camrail, 918 kilometres): Douala, Yaoundé, Bélabo and Ngaoundéré
- The Cameroonian population: 24 million inhabitants
- 1961: 5 million
- 1971: 7 million
- 1990: 12 million
- 2009: 19.5 million
- Population density of Cameroon: 50 inhabitants/km²
- Area of Cameroon: 475,650 km²
- The main tributary of the Niger River is the Benue river
- Cameroon is a Republic
- Independence of Cameroon from France: 1961
- Calling code of Cameroon: 237
- Code top-level domain of Cameroon: .cm
- Currency of Cameroon: CFA Franc (XAF)
The regions of Cameroon are (in brackets: capital/population in million inhabitants/area):
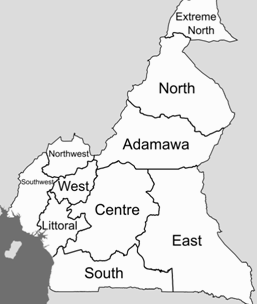
- Adamawa (Ngaoundéré/0.8/63,701)
- Centre (Yaoundé/3/68,953)
- East (Bertoua/0.7/109,002)
- North Extreme (Marua/3.1/34,263)
- Littoral (Douala/2.5/20,248)
- North (Garoua/1.6/66,000)
- West (Bafoussam/1.7/13,892)
- South (Ebolowa/0.6/47,191)
- North-West (Bamenda/1.7/13,892)
- South-West (Buéa/1.3/26,410)

Trade and Business Organisations (Cameroon)
- Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- OHADA
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Niger Basin Authority
- Bank of Central African States
- OIF
- European Union-Cameroon Free Trade Agreement
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- Commonwealth
- United Kingdom-Cameroon Free Trade Agreement

- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Development Bank
Main Cameroonian ethnicities:
In Cameroon, there are more than 280 ethnicities.
North of Cameroon
- Fula (foulbés): 2,9 million
- Kirdi
- Other ethnicities: Mafa, Toupouri, Moundang, Guiziga or Massa
West of Cameroon
- Bamileke
- Tikar
- Bamoun
South of Cameroon
- Beti (main group)
- Other ethnicities: Bassa, Boulousi, Dibom, Eton, Ewondo, Manguissa, Yabas
In Cameroon, they are large Hausa communities

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religions in the Republic of Cameroon:
-
Christianity (65% of the Cameroonian population)
- Catholics (38% of the Cameroonian population)
- Protestants (26% of the Cameroonian population)
- Sunni Islam (Adamawa, North, North Extreme and West of Cameroon)
- African Traditional Religions
Languages of Cameroon
In Cameroon, there are more than 242 languages.
The official languages of Cameroon are French (80% of the Cameroonian population) and English.
Cameroon, Ruanda and Mauritius are the bilingual African countries (French and English)
Francophone Regions:
- Adamawa (Ngaoundéré)
- Centre (Yaoundé)
- East (Bertoua)
- North Extreme (Marua)
- Littoral (Douala)
- North (Garoua)
- West (Bafoussam)
- South (Ebolowa)
Anglophone Regions (boundary with Nigeria):
- North-West (Bamenda)
- South-West (Buéa)
Others languages:
- Ngoumba, Gbaya, Yayoué, Bamoun, Tikar...
- Fula (Pular), in the North of Cameroon.
- Chamba Leko
History of Cameroon
The territory of the current Cameroon was colonized during the Neolithic era
- The first inhabitants were the Pygmy (hunter-gatherers Baka)
- 2nd millennium BC: Bantu migrations
- 1st millennium BC: Saharan farmers and shepherds arrive
- 500 AD: Sao Culture
- Kingdoms of Bamoun, Adamawa and Garoua
- 1472: arrival of the first Portuguese (Fernando Pó), Cameroon = Camarões in Portuguese
- Germans and Dutch also arrive
- Slave Trade
- 19th century: German protectorate
- Construction of the railroad and the port of Douala
- Cocoa, banana and coffee plantations.
- 1918: tutelage of the League of Nations (administration of France - eastern zone - and the United Kingdom - western zone)
- Movement of the UPC (Union of the populations of Cameroon), Ruben Um Nyobe
- Independence (France) in 1961
Higher Education in Cameroon
LMD System (Bachelor of Science-Master-Doctorate)- Cameroonian Ministry of Higher Education
Public Universities
- University of Yaoundé I (Ngoa Ekelle)
- University of Yaoundé II (Soa)
- University of Douala
- University of Buéa
- University of Dschang
- University of Ngaoundéré
- University of Bamenda
- University of Marua
Private Universities
- Catholic University of Central Africa (Yaoundé)
- University of the Mountains (Bangangté)
- Adventist University of Nanga-Eboko
- Protestant University of Central Africa (UPAC)
- University of South Yaoundé Ndi Samba
Cameroon is a member of the African and Malagasy Council for Higher Education (CAMES) and the Francophone University Agency (AUF)


 Tweet
Tweet


