Foreign Trade and Transport in Gabon, Libreville
Business in Gabon, Port-Gentil, Libreville, Franceville, Oyem, Logistics

Gabon (the Gabonese Republic) is a Central African country
- Libreville is the political and administrative capital of Gabon
- Port-Gentil is the Gabonese economic capital
- The largest Gabonese cities are Libreville, Franceville, Moanda, Oyem, Mouila, Lambaréné, Koulamoutou, Makokou and Tchibanga
- The main Gabonese resources are Petroleum, gas, iron, manganese and
forest resources (wood, 13% of the Gabonese GDP)
- Gabon is a member of the Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
- Hydrocarbons (Port-Gentil): 50% of the Gabonese GDP and 80% of the Gabonese exports
- Gabon is one of the three largest manganese exporters in the world
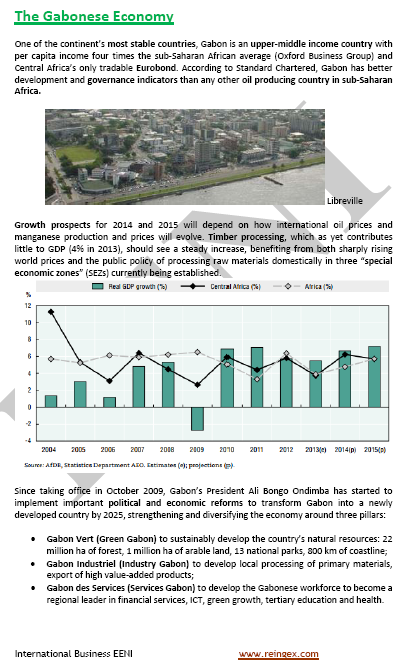
- Gabon is considered one of the most prosperous African countries
- The headquarters of the Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa (CEEAC) are in Libreville
- Gabon has the highest HDI (UN human development index) in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Currency of Gabon: CFA Franc (XAF)
- Gabon share borders with Cameroon (298 kilometres), Equatorial Guinea (350 kilometres) and the Republic of the Congo (1.903 kilometres)
Logistics and Transportation in Gabon
Only 10% of the Gabonese Road Transport network (9,170 kilometres) is paved.
No road is linking Libreville with Port-Gentil (river or maritime transport must be used).
National Road 2: Ambam (Cameroon), Gabon and Equatorial Guinea.
Anonébéré, Bifoun, Alembe, Viate, Mitzic, Bibasse, Oyem, Bitam, Éboro, Cameroon
Distance from Gabon to Dolisie (Republic of the Congo): 200 kilometres
Ports of Libreville, Mayumba and Port-Gentil
Port of Owendo (Libreville)

Franceville-Libreville Railway (Trans-Gabonese, 669 kilometres)
- Minerals and timber exports from Franceville region through the port of Owendo (Libreville)
River transport (1,600 kilometres) available from Port-Gentil and the Port of Owendo
International airports:
- Libreville
- Port-Gentil
- Franceville
 Gabon
Gabon


More information: International Trade and Business in Gabon, at EENI Global Business School Website.
- Gabon is a Republic
- Gabon obtained its Independence from France in 1960
- Calling code of Gabon: 241
- Code top-level domain of Gabon: .ga
- Gabonese population: 1,9 million inhabitants
- Gabonese Population density: 6.3 inhabitants/km²
- Area of Gabon: 267,667 km²
- Climate of Gabon: equatorial, warm and humid
- Lopé National Park (UNESCO World Heritage)
- The jungle covers 85% of the Gabonese territory
- Length of the Gabonese coastline: 885 kilometres
- Mount Bengoué: 1,070 meters
The main rivers of Gabon are:
- Ogooué (1,200 kilometres)
- Ivindo (500 kilometres)
- Ngounié (300 kilometres)
- Nyanga (600 kilometres)
- Komo (230 kilometres)
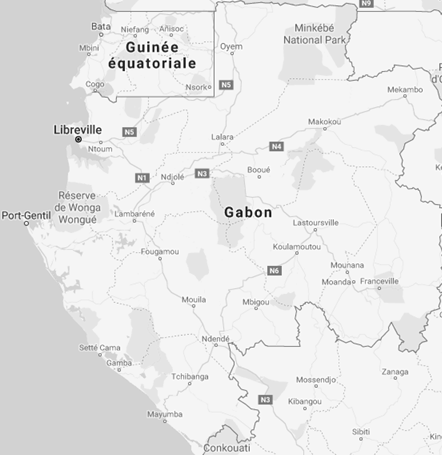
Provinces of Gabon
The nine regions of Gabon are (in brackets: capital/population in miles of inhabitants/area):

- Estuary (Libreville/895/20,740)
- Upper Ogooué (Franceville/250/36,547)
- Moyen-Ogooué (Lambaréné/69/18,535)
- Ngounié (Mouila/100/37,750)
- Nyanga (Tchibanga/52/21,285)
- Ogooué-Ivindo (Makokou/63/46,075)
- Ogooué-Lolo (Koulamoutou/65/25,380)
- Ogooué Maritime (Port-Gentil/157/22,890)
- Woleu-Ntem (Oyem/154/38,465)

Trade and Business Organisations (Gabon)
- Central African Economic and Monetary Community (CEMAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Organisation for the Harmonisation of Business Law in Africa (OHADA)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Bank of Central African States (BEA)
- OIF
- Organisation of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Development Bank
Main Gabonese ethnicities:
In Gabon, there are more than 50 ethnicities:
- Fang (32% of the Gabonese)
- Mpongwè (or Myènè, 15% of the Gabonese)
- Obamba (Mbédé, 14%)
- Punu (12%)
- Other ethnicities are Guisir, Vili, Nzebi, Bakota, Vungu and Téké

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religions in the Gabonese Republic
-
Christianity (73% of the Gabonese population)
- Catholics
- Protestants
- Islam (12%)
- African Traditional Religions
Languages of Gabon
In Gabon there are more than 50 Bantu languages:
- Baka (Pygmy language)
The official language of Gabon is French (80% of the Gabonese population)
History of Gabon
- Fossils (2.1 billion years old, Franceville)
- 400,000 years: traces of the first Gabonese oblations
- 5,000 years:
- First known inhabitants: the Pygmy
- Bantu Migrations (cattle breeding)
- 1st millennium BC: metallurgy
- Centuries XI - XVIII: the Mpongwe, a Bantu group, settle in the Estuary province
- 15th century: Portuguese (Gabão) and Dutch arrive
- Slave Trade (the Mpongwe)
- 19th century: the Fang (Bantu)
- 1886: French colony. Merged with the Congo (Gabon-Congo)
- 1910: integration in French Equatorial Africa
- 1946: overseas territory
- 1960: Independence of Gabon. Léon Mba (first minister)
- 1967: Omar Bongo (monoparty)
- 1990: multiparty
- 2009: Ali Bongo (son of Omar Bongo)
Higher Education in Gabon
LMD System (Bachelor of Science-Master-Doctorate)- Ministry Gabonese of Higher Education
- Bachelors of Science (BSc): L1 and L2
- Master: 2 years
- Doctorate: 2 years
Gabonese universities:
- University Omar Bongo (UOB) (Libreville)
- University Continental of Libreville
- Polytechnic University of Kougouleu
- University of Science and Techniques of Masuku
- Higher Institute of Technology (IST)
Gabon is a member of the African and Malagasy Council for Higher Education (CAMES) and the Francophone University Agency (AUF)


 Tweet
Tweet


