Foreign Trade and Transport in Guinea Conakry, Nzérékoré
Business and International Trade in Guinea Conakry: Kankan, Nzérékoré, Guéckédou, logistics

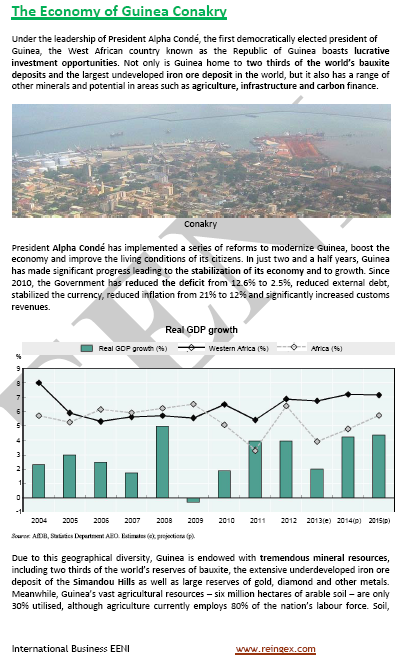
Guinea Conakry is a West African country
- The capital of Guinea is Conakry (3.6 million inhabitants)
- The most populated Guinean cities are Conakry, Kankan, Nzérékoré, Guéckédou, Kindia and Kissidougou
- Guinea Conakry is a very rich country in natural resources
- Guinea Conakry has 33% of the world bauxite reserves
- Guinean agricultural sector: 75% of the population (24% of the GDP)
- Currency of Guinea: Guinean Franc
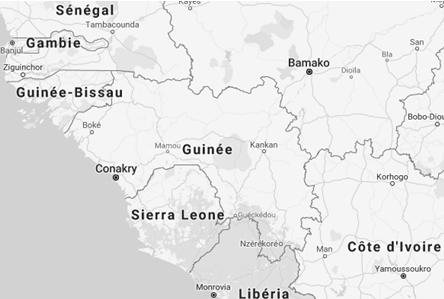
- Guinea share borders with six countries: Ivory Coast, Guinea-Bissau, Liberia, Mali, Senegal and Sierra Leone
Logistics and transport in Guinea:
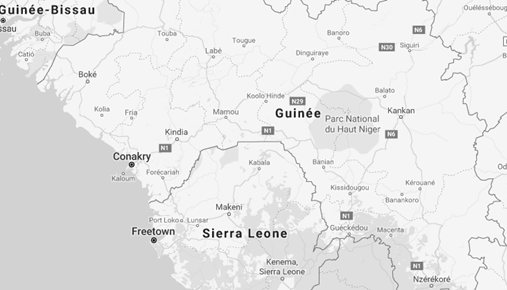
The main Roads of Guinea are:
- National Road N1: Conakry, Coyah, Kindia, Mamou, Dabola, Kouroussa, Kankan
- National Road N2: Mamou, Faranah, Kissidougou, Guékédou, Macenta, Nzérékoré, Lola
- Link to the capital of Ivory Coast (Yamoussoukro) during dry season
- National Road N4: Coyah, Forécariah, Farmoreya
- Link to Sierra Leone
- National Road N5: Mamou, Dalaba, Pita, Labé (Fouta Djalon)
- National Road N6: Kissidougou, Kankan, Siguiri, Bamako (Mali)
- National Road N20: Kamsar, Kolaboui, Boké
Access to the Dakar-Lagos Transport Corridor:
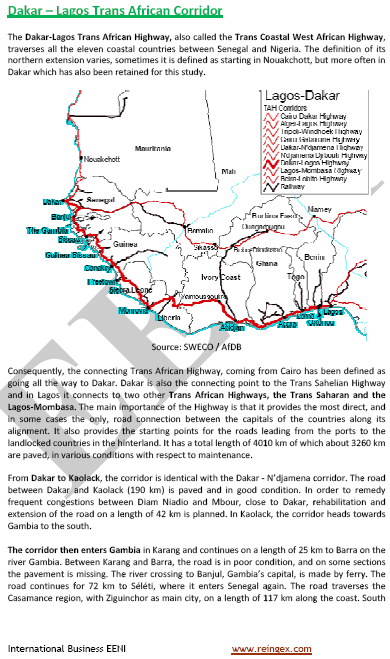
Conakry-Kankan Railway (105 kilometres, Bauxite Society of Kindia)
Conakry Autonomous Port (Managed by Bolloré)
Conakry International Airport
 Guinea
Guinea


More information: International Trade and Business in Guinea, at EENI Global Business School Website.
- The official language of Guinea is French
- African languages of Guinea are:
- Kissi (official)
- Pular
- Spoken in the Middle Guinea
- 40% of the Guinean population talks Pular
- Malinké
- Spoken in the Upper Guinea, in Kpelle and Forested Guinea (Guerzé)
- Soussou
- Spoken in the Lower Guinea and Conakry
- Total Guinean area 245,857 km²
- Total Guinean population: 13.2 million Guinean
- The impact of Slave Trade (16th century - 1850) was very strong in the population of Guinea
- Calling code of Guinea: 224
- Country code top-level domain: .gn
- The largest Guinean rivers are Senegal, Niger, Mano and Gambia
The Republic of Guinea is composed of four “natural” regions:
- Maritime Guinea (agriculture and mining, coastal area)
- Middle Guinea (livestock, mountainous area)/Moyenne-Guinée
- Fouta-Djalon Massif: 80,000 km², Mount Loura (1,532 m) - UNESCO world heritage
- Upper Guinea (agriculture, fishing, diamonds, gold. Savanna area)/Haute-Guinée
- Forested Guinea (agriculture, jungle area)/Guinée forestière
Guinean “administrative regions”:
- Government of Conakry
- Boké
- Kindia
- Mamou
- Faranah
- Kankan
- Labé
- Nzérékoré
The Guinean Historian Djibril Tamsir Niane, author of “The Epic of Soundiata”


Trade and Business Organisations (Guinea)
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- West African Monetary Zone (WAMZ)
- Niger Basin Authority
- Organisation for the Development of the Senegal River
- OHADA
- Mano River Union (MRU)
- Community of Sahel-Saharan States (CEN-SAD)
- Global System of Trade Preferences
- African Union
- AUDA-NEPAD
- Economic Commission for Africa
- African Development Bank

Religions and Global Business -
Religious diversity
Religion in Guinea:
- Sunni Islam: 85% of the Guinean population
- African Traditional Religions
- Christianity
Largest Guinean ethnicities:
- Fula: 40% of the Guinean population
- Malinke (Mandinka): 30%
- Susu: 20%
- Forestiers: 10%
History of Guinea
- 8th Century: population of Guinea by Baga and Nalou
- 11th Century: the Kingdom of Mandinka (vassal of the Ghana Empire)
- 13th Century: foundation of the Mali Empire by Soundiata Keïta
- 15th Century: collapse of the Mali Empire
- 8th Century: Islamisation of Guinea by Fula
- Participation in triangular trade (slaves, ivory and the aphrodisiac maniguette plant)
- Samory Touré (Mandinka, 1830): founder of the Wassoulou Empire
- Independence from France: October 1958
- Guinea Conakry was the first Sub-Saharan African country to obtain the independence
Higher Education in Guinea
- University of Conakry
- University Julius Nyerere of Kankan
- University Gamal Abdel Nasser of Conakry
- University General Lansana Conté
- University Kofi Annan of Guinea
- University Thierno Amadou Diallo
Guinea is a member of the African and Malagasy Council for Higher Education (CAMES)


 Tweet
Tweet

